Most individuals underestimate the complexity of headaches. Different types can have their own set of symptoms, occur for different reasons, and require different treatments.
Once you know what sort of headache you have, you and your doctor can discover the best therapy for it and even try to prevent it.
What exactly is a headache behind the eyes?
A headache is described as discomfort in any part of your head. A variety of headaches and other diseases can induce discomfort in the region behind one or between both eyes. In addition to pain, headaches in this location can induce light sensitivity and eye discomfort.
While headaches of any kind are frequent, understanding the underlying reason might help you manage them at home. It can also assist your doctor in making an accurate diagnosis and administering the most effective treatment.
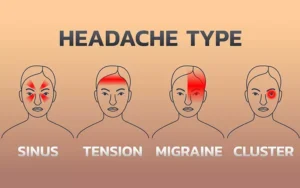
Common Types of Headaches
There are about over 150 different forms of headaches but they can be categorized into two groups;
Primary Headaches – headaches that are not caused by another illness. In this category are:
Cluster Headaches.
Migraines.
Posttraumatic Headaches.
Tension Headaches.
Sinus Aches and so on
Secondary headaches – caused by a different medical condition, such as:
Blood vessel disease in the brain.
A brain damage.
Blood pressure is high (hypertension).
Infection.
Medication abuse.
Congestion of the sinuses.
Trauma.
Tumor and so on
However the following are the most common types of headaches:
1. Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are the most prevalent type of headache in the globe. Any one is susceptible, although it is more frequent among women.
Tension headaches can be acute or persistent. Chronic tension headaches are defined as headaches that occur 15 or more days per month over a period of at least three months.
Tension headaches are characterized by a tightening sensation or pressure around the brow. Pain behind the eyes is also possible. Other symptoms related to this type of headache include:
- dull head pain
- scalp sensitivity
- ache in the neck and forehead
- increased light sensitivity
2. Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are abrupt, excruciating headaches that occur in “clusters” of 1 to 3 headaches each day. They generally happen at the same time every day for several weeks.
Cluster headaches can last anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour. They are defined as a burning or piercing painful feeling that is generally felt behind one eye. They frequently startle individuals out of their sleep.
Cluster headaches can also cause the following symptoms:
- red eyes
- swollen eyes
- red or swollen nose
- restlessness and agitation
- changes in heart rate and blood pressure
- sensitivity to light, sound, or smell
- excessive tearing
3. Migraines
Its is defined as “attacks” of moderate to severe throbbing pain on one side of the head that occur on a regular basis.
A migraine attack generally begins slowly and develops in intensity. Migraine attacks that go untreated can last anywhere from 4 to 72 hours.
In addition to discomfort, you may also experience:
- sensitivity to light
- sensitivity to noise
- sensitivity to odors
- eye pain
- dizziness/ nausea/weakness/vomiting
- impaired vision
- mood changes
- confusion exhaustion
- flashing or bright lights,
- the appearance of heat waves (aura)
- muscle weakness trouble speaking numbness on one side of the body
- loss of appetite
4. Eyestrain Headaches
Some incidences of headaches and soreness behind the eyes may be indicators of eyestrain or excessive eye strain.
Uncorrected vision problems or an excess of visual stress from looking at a computer, phone screen, television, or book can induce eyestrain. According to experts, headaches caused by eyestrain are trigger by a number of reasons, including:
- altered blinking patterns (reduced and incomplete blinking)
- excessive light exposure
- tiny font size
- sitting too near to a screen
5. Sinusitis
A sinus infection is caused by inflammation or congestion of the tissues that line your sinuses. This is known as sinusitis. As a result of nasal congestion, it might create headache-like symptoms.
Congestion is frequently accompanied with pressure across the forehead, cheeks, and behind the eye. Other symptoms you may feel, in addition to discomfort and pressure, include: Runny nose, stuffy nose, mucous streaming down throat (post-nasal drip), upper tooth pains, exhaustion, intensifying pain while lying down, fever etc
Other eye disorders that can produce discomfort behind the eye include:
- optic neuritis,
- inflammation of the optic nerve scleritis,
- severe inflammation of the white outer layer of the eye
- Graves’ disease is an autoimmune illness that causes discomfort, pressure, and sensitivity in the eyes.
- glaucoma, an eye disease affecting the optic nerve.
6. Posttraumatic Headaches
Posttraumatic stress headaches usually start 2-3 days after a head injury. You’ll feel:
- A dull ache that gets worse from time to time
- Vertigo
- Lightheadedness
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory problems
- Tiring quickly
- Irritability
Headaches may last for a few months. But if it doesn’t get better within a couple of weeks, call your doctor.
Potential Triggers
Different forms of headaches may have different triggers. The following are some of the most prevalent headache triggers:
- consuming alcohol
- hunger
- heavy perfume exposure odors
- a lot of noise
- dazzling lights
- fatigue
- hormonal shifts
- sleep deprivation
- mental anguish
- infection
- Traumatic incidents
A variety of factors can cause or trigger headaches behind the eyes or between the eyes. As a result, doctors frequently prescribe a comprehensive strategy that includes adopting lifestyle adjustments to lessen mental and emotional stress, as well as avoiding foods that may induce headaches.
Strategies for reducing headaches and accompanying symptoms are:
- everyday exercise
- To relieve stress, relax whenever possible.
- developing a regular sleep routine
- avoiding or limiting the consumption of processed foods
- maintaining enough hydration
- avoiding or limiting alcohol consumption
- abolition of tobacco usage
- avoiding or reducing caffeine consumption
Seek emergency medical assistance if your condition worsens or if you begin to encounter unusual symptoms in addition to your headache discomfort. It might be an indication of a more significant eyesight problem that has to be corrected or a medical problem that requires care.

How to check if the headache is related to your eyes…
Additional Treatments
Nondrug therapy can be used in addition to or instead of established treatments to help prevent headaches and alleviate symptoms. Nondrug therapies that may help improve or lessen headache symptoms include the following:
- undertaking biofeedback and stress management training to help you become more aware of, and better regulate, your body’s stress levels
- Cognitive Behaviour Therapy(CBT)- to assist manage stress, cope with symptoms, and identify headache causes.
- Acupuncture or pressure point therapy, to reduce stress and pain symptoms.
- Stress can be reduced by practicing mindfulness meditation.
- To reduce pain, apply cold or heat treatment to the head or back of the neck.
What are some effective home treatments for headaches behind the eyes?
- using a cold compress on the brow or back of the neck
- heat applied to the back of the neck
- self-acupressure
- relaxing in a dimly lit room
- Take a lot of fluids
Impressive ways to balance your hormones naturally

